Standards of Practice
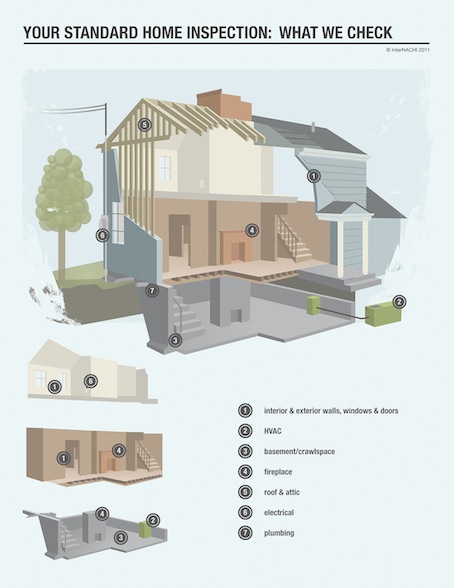 1. Definitions and Scope
1. Definitions and Scope
1.1. A home inspection is a non-invasive, visual examination of a residential dwelling, performed for a fee, which is designed to identify observed material defects within specific components of said dwelling. Components may include any combination of mechanical, structural, electrical, plumbing, or other essential systems or portions of the home, as identified and agreed to by the Client and Inspector, prior to the inspection process.
- A home inspection is intended to assist in the evaluation of the overall condition of the dwelling. The inspection is based on observations of the visible and apparent condition of the structure and its components on the date of the inspection, and not the prediction of future conditions.
- A home inspection will not reveal every concern that exists or ever could exist, but only those material defects observed on the day of the inspection.
1.2. A material defect is a condition of a residential real property, or any portion of it, that would have a significant, adverse impact on the value of the real property, or that involves an unreasonable risk to people on the property. The fact that a structural element, system or subsystem is near, at or beyond the end of its normal useful life is not, by itself, a material defect.
1.3. An inspection report shall describe and identify, in written format, the inspected systems, structures and components of the dwelling, and shall identify material defects observed. Inspection reports may contain recommendations regarding conditions reported or recommendations for correction, monitoring or further evaluation by professionals, but this is not required.
2. Limitations, Exceptions & Exclusions
2.1. Limitations:
- An inspection is not technically exhaustive.
- An inspection will not identify concealed or latent defects.
- An inspection will not deal with aesthetic concerns or what could be deemed matters of taste, cosmetic defects, etc.
- An inspection will not determine the suitability of the property for any use.
- An inspection does not determine the market value of the property or its marketability.
- An inspection does not determine the insurability of the property.
- An inspection does not determine the advisability or inadvisability of the purchase of the inspected property.
- An inspection does not determine the life expectancy of the property or any components or systems therein.
- An inspection does not include items not permanently installed.
- These Standards of Practice apply only to homes with four or fewer dwelling units.
2.2. Exclusions:
I. The inspector is not required to determine:
- property boundary lines or encroachments.
- the condition of any component or system that is not readily accessible.
- the service life expectancy of any component or system.
- the size, capacity, BTU, performance or efficiency of any component or system.
- the cause or reason of any condition.
- the cause for the need of repair or replacement of any system or component.
- future conditions.
- compliance with codes or regulations.
- the presence of evidence of rodents, animals or insects.
- the presence of mold, mildew, fungus or toxic drywall.
- the presence of airborne hazards.
- the presence of birds.
- the presence of other flora or fauna.
- the air quality.
- the existence of asbestos.
- the existence of environmental hazards.
- the existence of electromagnetic fields.
- the presence of hazardous materials including, but not limited to, the presence of lead in paint.
- any hazardous waste conditions.
- any manufacturers’ recalls or conformance with manufacturer installation, or any information included for consumer protection purposes.
- operating costs of systems.
- replacement or repair cost estimates.
- the acoustical properties of any systems.
- estimates of the cost to operate any given system.
II. The inspector is not required to operate:
- any system that is shut down.
- any system that does not function properly.
- or evaluate low-voltage electrical systems such as, but not limited to:
1. phone lines; 2. cable lines; 3. satellite dishes; 4. antennae; 5. lights; or 6. remote controls.- any system that does not turn on with the use of normal operating controls.
- any shut-off valves or manual stop valves.
- any electrical disconnect or over-current protection devices.
- any alarm systems.
- moisture meters, gas detectors or similar equipment.
III. The inspector is not required to:
- move any personal items or other obstructions, such as, but not limited to:
- throw rugs;
- furniture;
- floor or wall coverings;
- ceiling tiles;
- window coverings;
- equipment;
- plants;
- ice;
- debris;
- snow;
- water;
- dirt;
- foliage; or
- pets.
- dismantle, open or uncover any system or component.
- enter or access any area that may, in the opinion of the inspector, be unsafe.
- enter crawlspaces or other areas that are unsafe or not readily accessible.
- inspect underground items, such as, but not limited to, underground storage tanks or other indications of their presence, whether abandoned or actively used.
- do anything which, in the inspector’s opinion, is likely to be unsafe or dangerous to the inspector or others, or damage property, such as, but not limited to: walking on roof surfaces, climbing ladders, entering attic spaces, or negotiating with pets.
- inspect decorative items.
- inspect common elements or areas in multi-unit housing.
- inspect intercoms, speaker systems, radio-controlled security devices, or lawn irrigation systems.
- offer guarantees or warranties.
- offer or perform any engineering services.
- offer or perform any trade or professional service other than home inspection.
- research the history of the property, report on its potential for alteration, modification, extendibility or suitability for a specific or proposed use for occupancy.
- determine the age of construction or installation of any system structure or component of a building, or differentiate between original construction and subsequent additions, improvements, renovations or replacements.
- determine the insurability of a property.
- perform or offer Phase 1 environmental audits.
- inspect any system or component which is not included in these Standards.
3. Standards of Practice
3.1. Roof
I. The inspector shall inspect from ground level or eaves:
- the roof covering/materials;
- the gutters;
- the downspouts;
- the vents, flashing, skylights, chimney and other roof penetrations; and
- the general structure of the roof from the readily accessible panels, doors or stairs.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- walk on any pitched roof surface.
- predict the service life expectancy.
- inspect underground downspout diverter drainage pipes.
- remove snow, ice, debris or other conditions that prohibit the observation of the roof surfaces.
- move insulation.
- inspect antennae, satellite dishes, lightning arresters, de-icing equipment, or similar attachments.
- walk on any roof areas that appear, in the opinion of the inspector, to be unsafe.
- walk on any roof areas if it might, in the opinion of the inspector, cause damage.
- perform a water test.
- warrant or certify the roof.
- confirm proper fastening or installation of any roof-covering material.
3.2. ExteriorI. The inspector shall inspect:
- the exterior wall-covering material, flashing and trim;
- all exterior doors, decks, stoops, steps, stairs, porches, railings, eaves, soffits and fascias;
- and report as in need of repair any improper spacing between intermediate balusters, spindles and rails for steps, stairways, balconies and railings;
- a representative number of windows;
- the vegetation, surface drainage, and retaining walls when these are likely to adversely affect the structure;
- and describe the exterior wall covering.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- inspect or operate screens, storm windows, shutters, awnings, fences, outbuildings, or exterior accent lighting.
- inspect items, including window and door flashing, that are not visible or readily accessible from the ground.
- inspect or identify geological, geotechnical, hydrological or soil conditions.
- inspect recreational facilities or playground equipment.
- inspect seawalls, breakwalls or docks.
- inspect erosion-control or earth-stabilization measures.
- inspect for safety-type glass.
- inspect underground utilities.
- inspect underground items.
- inspect wells or springs.
- inspect solar, wind or geothermal systems.
- inspect swimming pools or spas.
- inspect waste water treatment systems, septic systems or cesspools.
- inspect irrigation or sprinkler systems.
- inspect drainfields or dry wells.
- determine the integrity of multiple-pane window glazing or thermal window seals.
- inspect any damaged glass.
3.3. Basement, Foundation & Crawlspace
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the basement;
- the foundation;
- the crawlspace;
- the visible structural components;
- and report on the location of under-floor access openings;
- and report any present conditions or clear indications of active water penetration;
- for wood in contact with or near soil;
- and report any general indications of foundation movement, such as, but not limited to: sheetrock cracks, brick cracks, out-of-square door frames, and floor slopes;
- and report on any cutting, notching and boring of framing members that may present a structural or safety concern.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- enter any crawlspaces that are not readily accessible or where entry could cause damage or pose a hazard to the inspector.
- move stored items or debris.
- operate sump pumps with inaccessible floats.
- identify size, spacing, span, location or determine adequacy of foundation bolting, bracing, joists, joist spans or support systems.
- provide any engineering or architectural service.
- report on the adequacy of any structural system or component.
3.4. HeatingI. The inspector shall inspect:
- the heating systems, using normal operating controls, and describe the energy source and heating method;
- and report as in need of repair heating systems that do not operate;
- and report if the heating systems are deemed inaccessible.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- inspect or evaluate the interior of flues or chimneys, fire chambers, heat exchangers, combustion air systems, fresh air intakes, humidifiers, dehumidifiers, electronic air filters, geothermal systems, or solar heating systems.
- inspect fuel tanks or underground or concealed fuel supply systems.
- determine the uniformity, temperature, flow, balance, distribution, size, capacity, BTU, or supply adequacy of the heating system.
- light or ignite pilot flames.
- activate heating, heat pump systems or other heating systems when ambient temperatures or other circumstances are not conducive to safe operation or may damage the equipment.
- override electronic thermostats.
- evaluate fuel quality.
- verify thermostat calibration, heat anticipation, or automatic setbacks, timers, programs or clocks.
3.5. Cooling
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the central cooling equipment using normal operating controls.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- determine the uniformity, temperature, flow, balance, distribution, size, capacity, BTU, or supply adequacy of the cooling system.
- inspect window units, through-wall units, or electronic air filters.
- operate equipment or systems if the exterior temperature is below 65° Fahrenheit, or when other circumstances are not conducive to safe operation or may damage the equipment.
- inspect or determine thermostat calibration, cooling anticipation, or automatic setbacks or clocks.
- examine electrical current, coolant fluids or gases, or coolant leakage.
3.6. Plumbing
I. The inspector shall:
- determine and report whether the water supply is public or private;
- verify the presence and identify the location of the main water shut-off valve;
- inspect the water heating equipment, including venting connections, energy source supply system, and seismic bracing, and verify the presence or absence of temperature-pressure relief valves and/or Watts 210 valves;
- inspect toilets for proper operation;
- water-test sinks, tubs and showers for functional drainage;
- inspect the interior water supply, including all fixtures and faucets;
- inspect the drain, waste and vent systems, including all fixtures;
- describe any visible fuel-storage systems;
- inspect the drainage sump pumps, and test pumps with accessible floats;
- inspect and describe the location of the main water supply and main fuel shut-off valves.
- inspect and report as in need of repair deficiencies in the water supply by viewing the functional flow in two fixtures operated simultaneously;
- inspect and report as in need of repair deficiencies in installation of hot and cold water faucets;
- inspect and report as in need of repair any mechanical drain stops that are missing or do not operate if installed in sinks, lavatories and tubs; and
- inspect and report any evidence that toilets are damaged, have loose connections to the floor, leak, or have tank components that do not operate.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- light or ignite pilot flames.
- determine the size, temperature, age, life expectancy or adequacy of the water heater.
- inspect the interior of flues or chimneys, combustion air systems, water softener or filtering systems, well pumps or tanks, safety or shut-off valves, floor drains, lawn sprinkler systems, or fire sprinkler systems.
- determine the exact flow rate, volume, pressure, temperature or adequacy of the water supply.
- determine the water quality, potability or reliability of the water supply or source.
- open sealed plumbing access panels.
- inspect clothes washing machines or their connections.
- operate any valve.
- test shower pans, tub and shower surrounds or enclosures for leakage.
- evaluate the compliance with conservation, energy, or building standards, or the proper design or sizing of any water, waste or venting components, fixtures or piping.
- determine the effectiveness of anti-siphon, back-flow prevention or drain-stop devices.
- determine whether there are sufficient cleanouts for effective cleaning of drains.
- evaluate fuel storage tanks or supply systems.
- inspect wast water treatment systems.
- inspect water treatment systems or water filters.
- inspect water storage tanks, pressure pumps or bladder tanks.
- evaluate wait-time to obtain hot water at fixtures, or perform testing of any kind to water heater elements.
- evaluate or determine the adequacy of combustion air.
- test, operate, open or close safety controls, manual stop valves and/or temperature or pressure-relief valves.
- examine ancillary systems or components, such as, but not limited to, those related to solar water heating and hot water circulation.
3.7. Electrical
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the service drop/lateral;
- the meter socket enclosures;
- the means for disconnecting the service main;
- and describe the service disconnect amperage rating, if labeled;
- panelboards and over-current devices (breakers and fuses);
- and report on any unused circuit breaker panel openings that are not filled;
- the service grounding and bonding;
- a representative number of switches, lighting fixtures and receptacles, including receptacles observed and deemed to be arc-fault circuit interrupter or AFCI-protected using the AFCI test button, where possible;
- and test all ground-fault circuit interrupter receptacles and circuit breakers observed and deemed to be GFCIs using a GFCI tester, where possible;
- and report the presence of solid conductor aluminum branch circuit wiring, if readily visible;
- and report on any tested receptacles in which power was not present, polarity was incorrect, the cover was not in place, the GFCI devices were not properly installed or did not operate properly, evidence of arcing or excessive heat, and where the receptacle was not grounded or was not secured to the wall;
- the service entrance conductors and the condition of the conductor insulation;
- and report the absence of smoke detectors; and
- service entrance cables, and report as in need of repair deficiencies in the integrity of the insulation, drip loop, or separation of conductors at weatherheads and clearances from grade and rooftops.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- insert any tool, probe or device into the main panelboard, sub-panels, distribution panelboards, or electrical fixtures.
- operate electrical systems that are shut down.
- remove panelboard cabinet covers or dead fronts, if they are not readily accessible.
- operate or re-set over-current protection devices or overload devices.
- operate non-accessible smoke detectors.
- measure or determine the amperage or voltage of the main service equipment, if not visibly labeled.
- inspect the fire and alarm system or components.
- inspect the ancillary wiring or remote control devices.
- activate any electrical systems or branch circuits that are not energized.
- inspect low-voltage systems, electrical de-icing tapes, swimming pool wiring, or any time-controlled devices.
- verify the service ground.
- inspect private or emergency electrical supply sources, including, but not limited to: generators, windmills, photovoltaic solar collectors, or battery or electrical storage facility.
- inspect spark or lightning arrestors.
- inspect or test de-icing equipment.
- conduct voltage-drop calculations.
- determine the accuracy of labeling.
- inspect exterior accent lighting.
3.8. Fireplace
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the fireplace, and open and close the damper door, if readily accessible and operable;
- hearth extensions and other permanently installed components;
- and report as in need of repair deficiencies in the lintel, hearth and material surrounding the fireplace, including the fireplace opening’s clearance from visible combustible materials.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- inspect the flue or vent system.
- inspect the interior of chimneys or flues, fire doors or screens, seals or gaskets, or mantels.
- determine the need for a chimney sweep.
- operate gas fireplace inserts.
- light pilot flames.
- determine the appropriateness of any installation.
- inspect automatic fuel-feed devices.
- inspect combustion and/or make-up air devices.
- inspect heat-distribution assists, whether gravity-controlled or fan-assisted.
- ignite or extinguish fires.
- determine the adequacy of drafts or draft characteristics.
- move fireplace inserts, stoves or firebox contents.
- perform a smoke test.
- dismantle or remove any component.
- perform a National Fire Prevention Association (NFPA)-style inspection.
- perform a Phase I fireplace and chimney inspection.
3.9. Attic, Ventilation & Insulation
I. The inspector shall inspect:
- the insulation in unfinished spaces;
- for the presence of attic ventilation;
- mechanical ventilation systems;
- and report on the general absence or lack of insulation in unfinished spaces.
II. The inspector is not required to:
- enter the attic or any unfinished spaces that are not readily accessible, or where entry could cause damage or pose a safety hazard to the inspector, in his or her opinion.
- move, touch or disturb insulation.
- move, touch or disturb vapor retarders.
- break or otherwise damage the surface finish or weather seal on or around access panels or covers.
- identify the composition or exact R-value of insulation material.
- activate thermostatically operated fans.
- determine the types of materials used in insulation or wrapping of pipes, ducts, jackets, boilers or wiring.
- determine the adequacy of ventilation.
3.10. Doors, Windows & Interior
I. The inspector shall:
- open and close a representative number of doors and windows;
- inspect the walls, ceilings, steps, stairways and railings;
- and report as in need of repair any improper spacing between intermediate balusters, spindles and rails for steps, stairways and railings;
- inspect garage doors and garage door openers by operating using the installed automatic door control;
- and report as improper any photoelectric safety sensor that fails to respond adequately to testing;
- and report as in need of repair any door locks or side ropes that have not been removed or disabled when the garage door opener is in use;
II. The inspector is not required to:
- inspect paint, wallpaper, window treatments or finish treatments.
- inspect central vacuum systems.
- inspect for safety glazing.
- inspect security systems or components.
- evaluate the fastening of countertops, cabinets, sink tops or fixtures.
- move furniture, stored items, or any coverings, such as carpets or rugs, in order to inspect the concealed floor structure.
- move suspended-ceiling tiles.
- inspect or move any household appliances.
- inspect or operate equipment housed in the garage, except as otherwise noted.
- verify or certify proper operation of any pressure-activated auto-reverse or related safety feature of a garage door.
- operate or evaluate any security bar release and opening mechanisms, whether interior or exterior, including their compliance with local, state or federal standards.
- operate any system, appliance or component that requires the use of special keys, codes, combinations or devices.
- operate or evaluate self-cleaning oven cycles, tilt guards/latches, or signal lights.
- inspect microwave ovens or test leakage from microwave ovens.
- operate or examine any sauna, steam-generating equipment, kiln, toaster, ice maker, coffee maker, can opener, bread warmer, blender, instant hot-water dispenser, or other small, ancillary devices.
- inspect elevators.
- inspect remote controls.
- inspect appliances.
- inspect items not permanently installed.
- discover firewall compromises.
- inspect pools, spas, recreational or stand-alone equipment.
- come into contact with any pool or spa water in order to determine the system’s structure or components.
- determine the adequacy of whirlpool or spa jets, water force, or bubble effect.
- determine the structural integrity or leakage of a pool or spa.
4. Glossary of Terms
4.1. accessible: can be approached or entered by the inspector safely, without difficulty, fear or danger.
4.2. activate: to turn on, supply power, or enable systems, equipment or devices to become active by normal operating controls. Examples include turning on the gas or water supply valves to the fixtures and appliances, and activating electrical breakers or fuses.
4.3. adversely affect: to constitute, or potentially constitute, a negative or destructive impact.
4.4. alarm system: warning devices, installed or freestanding, including, but not limited to: carbon monoxide detectors, flue gas and other spillage detectors, security equipment, ejector pumps, and smoke alarms.
4.5. appliance: a household device operated by the use of electricity or gas. Not included in this definition are components covered under central heating, central cooling or plumbing.
4.6. architectural service: any practice involving the art and science of building design for construction of any structure or grouping of structures, and the use of space within and surrounding the structures or the design, design development, preparation of construction contract documents, and administration of the construction contract.
4.7. component: a permanently installed or attached fixture, element or part of a system.
4.8. condition: the visible and conspicuous state of being of an object.
4.9. crawlspace: the area within the confines of the foundation and between the ground and the underside of the lowest floor’s structural component.
4.10. decorative: ornamental; not required for the operation of essential systems or components of a home.
4.11. describe: to report in writing a system or component by its type or other observed characteristics in order to distinguish it from other components used for the same purpose.
4.12. determine: to arrive at an opinion or conclusion pursuant to examination.
4.13. dismantle: to open, take apart or remove any component, device or piece that would not typically be opened, taken apart or removed by an ordinary occupant.
4.14. engineering service: any professional service or creative work requiring engineering education, training and experience, and the application of special knowledge of the mathematical, physical and engineering sciences to such professional service or creative work as consultation, investigation, evaluation, planning, design and supervision of construction for the purpose of assuring compliance with the specifications and design, in conjunction with structures, buildings, machines, equipment, works or processes.
4.15. enter: to go into an area to observe visible components.
4.16. evaluate: to assess the systems, structures and/or components of a dwelling.
4.17. examine: to visually look (see inspect).
4.18. foundation: the base upon which the structure or wall rests; usually masonry, concrete or stone, and generally partially underground.
4.19. function: the action for which an item, component or system is specially fitted or used, or for which an item, component or system exists; to be in action or perform a task.
4.20. functional: performing, or able to perform, a function.
4.21. home inspection: the process by which an inspector visually examines the readily accessible systems and components of a home and operates those systems and components utilizing these Standards of Practice as a guideline.
4.22. household appliances: kitchen and laundry appliances, room air conditioners, and similar appliances.
4.23. inspect: to visually look at readily accessible systems and components safely, using normal operating controls, and accessing readily accessible panels and areas, in accordance with these Standards of Practice.4.24. inspected property: the readily accessible areas of the buildings, site, items, components and systems included in the inspection.4.25. inspector: one who performs a real estate inspection.
4.26. installed: attached or connected such that the installed item requires a tool for removal.
4.27. material defect: a condition of a residential real property or any portion of it that would have a significant adverse impact on the value of the real property or that involves an unreasonable risk to people on the property. The fact that a structural element, system or subsystem is near, at or beyond the end of its normal useful life is not, by itself, a material defect.
4.28. normal operating controls: devices, such as thermostats, that would be operated by ordinary occupants which require no specialized skill or knowledge.
4.29. observe: to see through visually directed attention.
4.30. operate: to cause systems to function or turn on with normal operating controls.
4.31. readily accessible: an item or component that is, in the judgment of the inspector, capable of being safely observed without the removal of obstacles, detachment or disengagement of connecting or securing devices, or other unsafe or difficult procedures to gain access.
4.32. recreational facilities: spas, saunas, steam baths, swimming pools, tennis courts, playground equipment, and other exercise, entertainment and athletic facilities.
4.33. report: a written communication (possibly including images) of any material defects observed during the inspection.
4.34. representative number: a sufficient number to serve as a typical or characteristic example of the item(s) inspected.
4.35. safety glazing: tempered glass, laminated glass, or rigid plastic.
4.36. shut down: turned off, unplugged, inactive, not in service, not operational, etc.
4.37. structural component: a component that supports non-variable forces or weights (dead loads) and variable forces or weights (live loads).
4.38. system: an assembly of various components which function as a whole.
4.39. technically exhaustive: a comprehensive and detailed examination beyond the scope of a real estate home inspection that would involve or include, but would not be limited to: dismantling, specialized knowledge or training, special equipment, measurements, calculations, testing, research, analysis, or other means.
4.40. unsafe: a condition in a system or component that is judged to be a significant risk of personal injury during normal, day-to-day use. The risk may be due to damage, deterioration, improper installation, or a change in accepted residential construction standards.
4.41. verify: to confirm or substantiate.





